I was digging through some old 2002 powerpoint slides for an article on active skin and stumbled across probably the worst illustration I have ever done, though in my defense, I was documenting a great many ideas that day and spent only a few minutes on it:
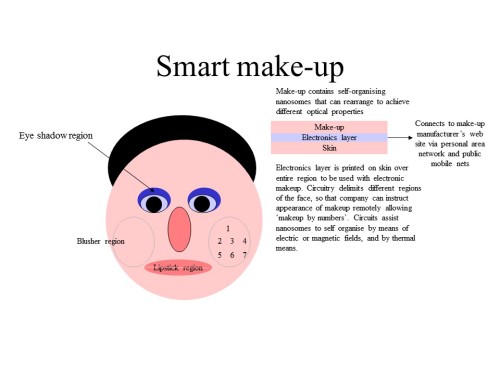
If a woman ever looks like this, and isn’t impersonating a bald Frenchman, she has more problems to worry about than her make-up. The pic does however manage to convey the basic principle, and that’s all that is needed for a technical description. The idea is that her face can be electronically demarked into various makeup regions and the makeup on those regions can therefore adopt the appropriate colour for that region. In the pic ‘nanosomes’ wasn’t a serious name, but a sarcastic take on the cosmetics industry which loves to take scientific sounding words and invent new ones that make their products sound much more high tech than they actually are. Nanotech could certainly play a role, but since the eye can’t discern features smaller than 0.1mm, it isn’t essential. This is no longer just an idea, companies are now working on development of smart makeup, and we already have prototype electronic tattoos, one of the layers I used for my active skin but again based on an earlier vision.
The original idea didn’t use electronics, but simply used self-organisation tech I’d designed in 1993 on an electronic DNA project. Either way would work, but the makeup would be different for each.
The electronic layer, if required, would most likely be printed onto the skin at a beauty salon, would be totally painless, last weeks and could take only a few minutes to print. It extends IoT to the face.
Both mechanisms could use makeup containing flat plates that create colour by diffraction the same way the scales on a butterfly does. That would make an excellent colour pallet. Beetles produce colour a different way and that would work too. Or we could copy squids or cuttlefish. Nature has given us many excellent start points for biomimetics, and indeed the self-organisation principles were stolen from nature too. Nature used hormone gradients to help your cells differentiate when you were an embryo. If nature can arrange the rich microscopic detail of every part of your face, then similar techniques can certainly work for a simple surface layer of make-up. Having the electronic underlay makes self organisation easier but it isn’t essential. There are many ways to implement self organisation in makeup and only some of them require any electronics at all, and some of those would use electronic particles embedded in the make-up rather than an underlay.
An electronic underlay can be useful to provide the energy for a transition too, and that allows the makeup to change colour on command. That means in principle that a woman could slap the makeup all over her face and touch a button on her digital mirror (which might simply be a tablet or smart phone) and the make-up would instantly change to be like the picture she selected. With suitable power availability, the make-up could be a full refresh rate video display, and we might see teenagers walking future streets wearing kaleidoscopic make-up that shows garish cartoon video expressions and animates their emoticons. More mature women might choose different appearances for different situations and they could be selected manually via an app or gesture or automatically by predetermined location settings.
Obviously, make-up is mostly used on the face, but once it becomes the basis of a smear-on computer display, it could be used on any part of the body as a full touch sensitive display area, e.g. the forearm.
Although some men already wear makeup, many more might use smart make-up as its techie nature makes it more acceptable.